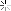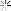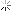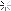Men of 7th Division hugging ground as they use flame throwers to smoke out Japanesefrom block house while other soldiers behind them wait w. rifles, ready in case Japanese come out, during WWII. Marshall Islands.
Location:Kwajalein Atoll, Marshall Islands
Date taken:February 4, 1944
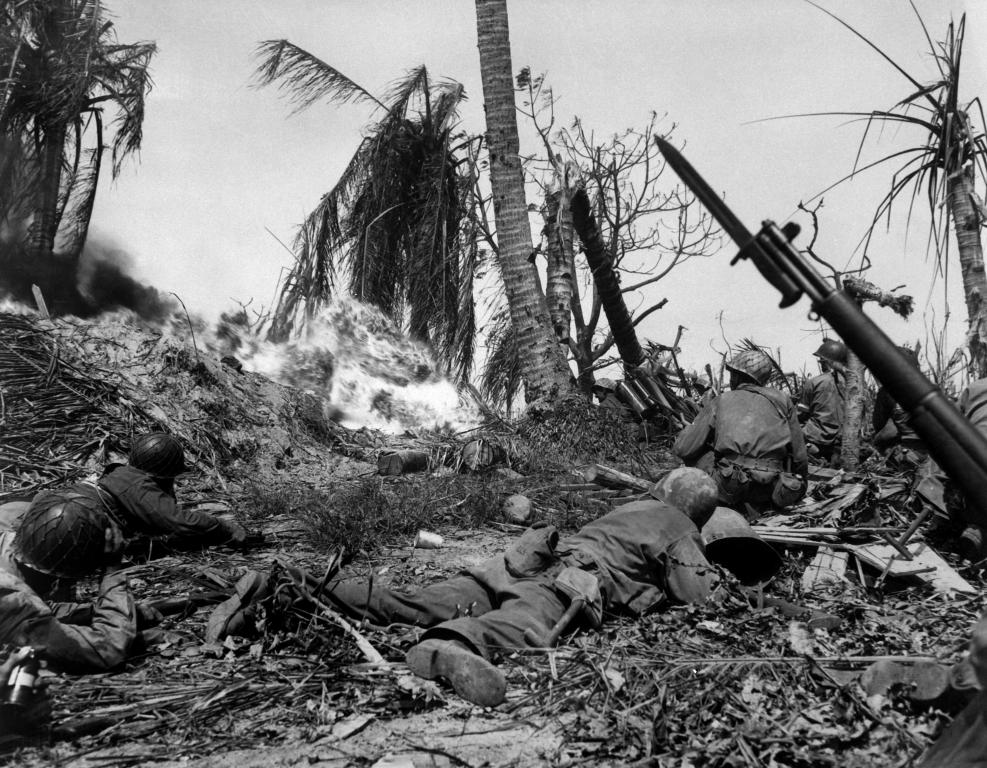
Kwajalein
Date taken: February 1944
Photographer:George Strock
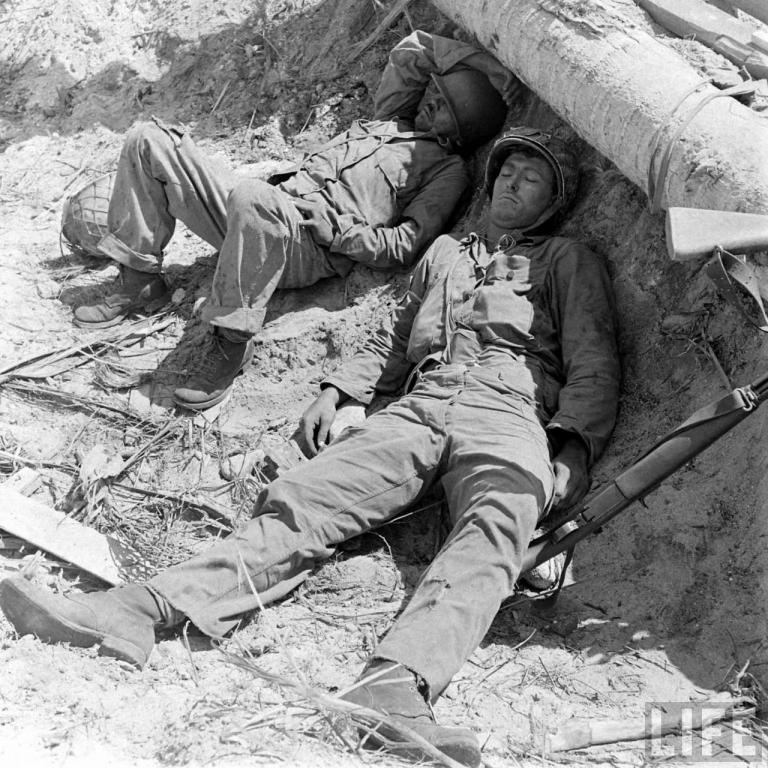
Kwajalein
Date taken: February 1944
Photographer:George Strock
The Battle of Kwajalein was a battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II, fought from 31 January-3 February 1944, on Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands. Employing the hard-learned lessons of the battle of Tarawa, the United Stateslaunched a successful twin assault on the main islands of Kwajalein in the south and Roi-Namur in the north. The Japanese defenders put up a stiff resistance though outnumbered and under-prepared. The determined defense of Roi-Namur left only 51 survivors of an original garrison of 3,500.
For the U.S., the battle represented both the next step in its island-hopping march to Japan and a significant moral victory because it was the first time the U.S. penetrated the "outer ring" of the Japanese Pacific sphere. For the Japanese, the battle represented the failure of the beach-line defense. Japanese defenses became prepared in depth, and the battles of Peleliu, Guam, and the Marianas proved far more costly to the U.S.
The U.S. forces for the landings were Rear Admiral Richmond K. Turner's 5th Amphibious Force, and Major General Holland M. Smith's V Amphibious Corps, which comprised the 4th Marine Division commanded by Maj. Gen. Harry Schmidt, the 7th Infantry Division commanded by Maj.Gen. Charles H. Corlett, plus the 22nd Marines, 106th Infantry, and the 111th Infantry regiments. The 4th and 7th Divisions were assigned to the initial landings at Kwajalein, while the 2nd Battalion of the 106th was assigned to the simultaneous capture of Majuro Atoll. The rest of the 106th and the 22nd Marines were in reserve for Kwajalein, while awaiting the following assault on Eniwetok, scheduled for three months later.
The 7th Infantry Division began by capturing the small islands labeled Carlos, Carter, Cecil, and Carlson on 31 January, which were used as artillery bases for the next day's assault. Kwajalein Island is 2.5 mi (4.0 km) long but only 880 yd (800 m) wide. There was therefore no possibility of defence in depth and the Japanese planned to counter-attack the landing beaches. They had not realized until the battle of Tarawa that American amphibious vehicles could cross coral reefs and so land on the lagoon side of an atoll; accordingly the strongest defences on Kwajalein faced the ocean. The bombardment by battleships, B-24 bombers from Apamama, and artillery on Carlson was devastating. The U.S. Army history of the battle quotes a participant as saying that "the entire island looked as if it had been picked up 20,000 feet and then dropped." By the time the 7th Division landed on Kwajalein Island on 1 February, there was little resistance; by night the Americans estimated that only 1,500 of the original 5,000 defenders were still alive.
On the north side of the atoll, the 4th Marine Division followed the same plan, first capturing islets Ivan, Jacob, Albert, Allen, and Abraham on 31 January, and landing on Roi-Namur on 1 February. The airfield on Roi (the eastern half) was captured quickly, and Namur (the western half) fell the next day. The worst setback came when a Marine demolition team threw a satchel charge of high explosives into a Japanese bunker which turned out to be a torpedo warhead magazine. The resulting explosion killed twenty Marines and wounded dozens more. Only 51 of the original 3,500 Japanese defenders of Roi-Namur survived to be captured.Information

Warning: This is a relatively older thread
This discussion is older than 360 days. Some information contained in it may no longer be current.
- Knowledge Library

- MKL Entry of the Month
- Australia
- Austro-Hungarian Empire
- Canada
- Czechoslovakia
- Denmark
- Finland
- France/Belgium
- Germany
- Italy
- Japan
- Norway
- Russia
- South America
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- United Kingdom
- United States
- Yugoslavia
- Is my rifle authentic or a fake?
- Jay Currah's Lee Enfield Web Site
- On-line Service Records (Canada)
- Technical Articles/Research
- Forum
- Classifieds

- What's New?
-
Photo Gallery

- Photo Gallery Options
- Photo Gallery Home
- Search Photo Gallery List
-
Photo Gallery Search
- Video Club

- iTrader






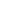






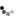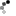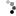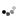
 PM
PM