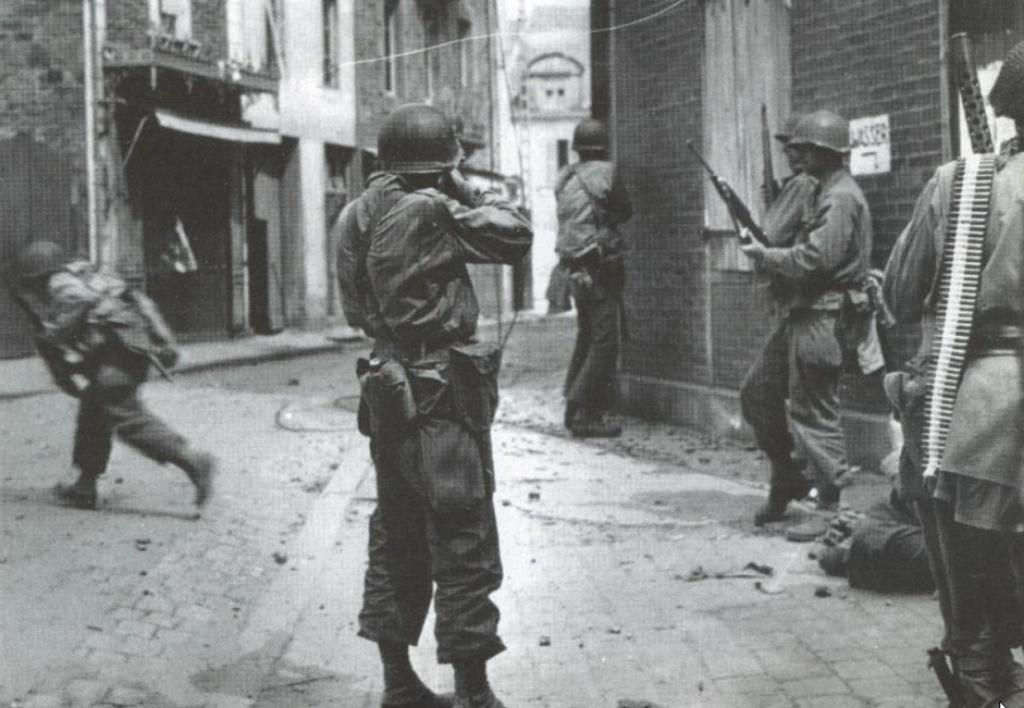
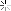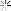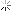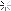Troops of the 83rd Infantry Division mounting tanks of the 2nd Armored Division, US 9th Army, in preparation for a continuation of their drive toward the Rhine River in Germany
The 83d Infantry Division arrived in Englandon 16 April 1944. After training in Wales, the division landed at Omaha Beach, 18 June 1944, and entered the hedgerow struggle south of Carentan, 27 June. Taking the offensive, the 83d reached the St. Lo-Periers Road, 25 July, and advanced 8 miles (13 km) against strong opposition as the Normandy campaign ended.
After a period of training, elements of the division took Châteauneuf-d'Ille-et-Vilaine, 5 August, and Dinard, 15 August, and approached the heavily fortified area protecting St. Malo. Intense fighting reduced enemy strong points and a combined attack against the Citadel Fortress of St. Servan caused its surrender, 17 August. While elements moved south to protect the north bank of the Loire River, the main body of the division concentrated south of Rennes for patrolling and reconnaissance activities. Elements reduced the garrison at Ile de Cézembre, which surrendered, 2 September. On 16 September 1944: the only surrender of a German Major General B. H. Elster to US-troops with 18,850 men and 754 officers at the Loire bridge of Beaugency. The movement into Luxembourg was completed on 25 September. Taking Remich on the 28th and patrolling defensively along the Moselle, the 83d resisted counterattacks and advanced to the Siegfried Line defenses across the Sauer after capturing Grevenmacher and Echternach, 7 October. As the initial movement in operation "Unicorn," the division took Le Stromberg Hill in the vicinity of Basse Konz against strong opposition, 5 November, and beat off counterattacks.
Moving to the Hurtgen Forest, the 83d thrust forward from Gressenich to the west bank of the Roer. It entered the Battle of the Bulge, 27 December, striking at Rochefort and reducing the enemy salient in a bitter struggle. The division moved back to Belgium and the Netherlands for rehabilitation and training, 22 January 1945. On 1 March, the 83d advanced toward the Rhine in Operation Grenade, and captured Neuss. The west bank of the Rhine from north of Oberkassel to the Erft Canal was cleared and defensive positions established by 2 March and the division renewed its training. The 83d crossed the Rhine south of Wesel, 29 March, and advanced across the Munster Plain to the Weser, crossing it at Bodenwerder. As opposition disintegrated, Halle fell on 6 April. The division crossed the Leine, 8 April, and attacked to the east, pushing over the Harz Mountain region and advancing to the Elbe at Barby. That city was taken on the 13 April. The 83rd established a bridgehead over the river.
On 11 April 1945 the 83rd encountered Langenstein, a subcamp of the Buchenwald concentration camp. At the camp, the troops found approximately 1,100 inmates. The inmates were malnourished and in extremely poor physical condition. The 83rd reported the death rate at the camp to be 500 per month. Also, that the prisoners had been forced to work 16 hour days in nearby mines, and were shot if they became too weak to work. After liberation, the death rate continued at approximately 25–50 people per day, due to the severe physical debilitation of the prisoners.
To slow the spread of sickness and death, the 83rd ordered the local German mayor to supply the camp with food and water. Also, medical supplies were requisitioned from the U.S. Army's 20th Field Hospital. In addition, the 83rd recovered documents for use by war crimes investigators.
Casualities
Killed in action 2,850
Died of wounds 425
Total killed 3,275
Seriously wounded in action 3,809
Slightly wounded in action 6,096
Seriously injured in action 111
Slightly injured in action 1,044
Total wounded and injured 11,060
Captured 177
Missing in action 501
Replacements
Returned to Duty 10,187
Reinforcements 15,736
Total Replacements 25,923
Enemy Equipment Destroyed
Tanks 480
Planes 61
Supply Trains 29
Artillery Pieces 966
Miscellaneous
Days of contact with the enemy 270
Prisoners captured 82,146
Battlefield Commissions 75
Rounds of artillery fired 410,251
Rounds of small arms and 21,899,955 mortars fired
Decorations and Awards
Congressional Medal of Honor 1:
Sgt Ralph Neppel
Sergeant Neppel's official Medal of Honor citation reads:
He was leader of a machinegun squad defending an approach to the village of Birgel, Germany, on 14 December 1944, when an enemy tank, supported by 20 infantrymen, counterattacked. He held his fire until the Germans were within 100 yards and then raked the foot soldiers beside the tank killing several of them. The enemy armor continued to press forward and, at the pointblank range of 30 yards, fired a high-velocity shell into the American emplacement, wounding the entire squad. Sgt. Neppel, blown 10 yards from his gun, had 1 leg severed below the knee and suffered other wounds. Despite his injuries and the danger from the onrushing tank and infantry, he dragged himself back to his position on his elbows, remounted his gun and killed the remaining enemy riflemen. Stripped of its infantry protection, the tank was forced to withdraw. By his superb courage and indomitable fighting spirit, Sgt. Neppel inflicted heavy casualties on the enemy and broke a determined counterattack.
Distinguished Service Medal 1
Distinguished Service Cross 5
Legion of Merit 5
Silver Stars 798
Soldier's Medal 34
Bronze Star Medal 7,776
Purple Heart 4,747
Medical Badge 271
Meritorious Service
Unit Plaque 20
Air Medal 106
Plus 18 British Awards and 65 FrenchAwards
Information

Warning: This is a relatively older thread
This discussion is older than 360 days. Some information contained in it may no longer be current.
- Knowledge Library

- MKL Entry of the Month
- Australia
- Austro-Hungarian Empire
- Canada
- Czechoslovakia
- Denmark
- Finland
- France/Belgium
- Germany
- Italy
- Japan
- Norway
- Russia
- South America
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- United Kingdom
- United States
- Yugoslavia
- Is my rifle authentic or a fake?
- Jay Currah's Lee Enfield Web Site
- On-line Service Records (Canada)
- Technical Articles/Research
- Forum
- Classifieds

- What's New?
-
Photo Gallery

- Photo Gallery Options
- Photo Gallery Home
- Search Photo Gallery List
-
Photo Gallery Search
- Video Club

- iTrader












 PM
PM