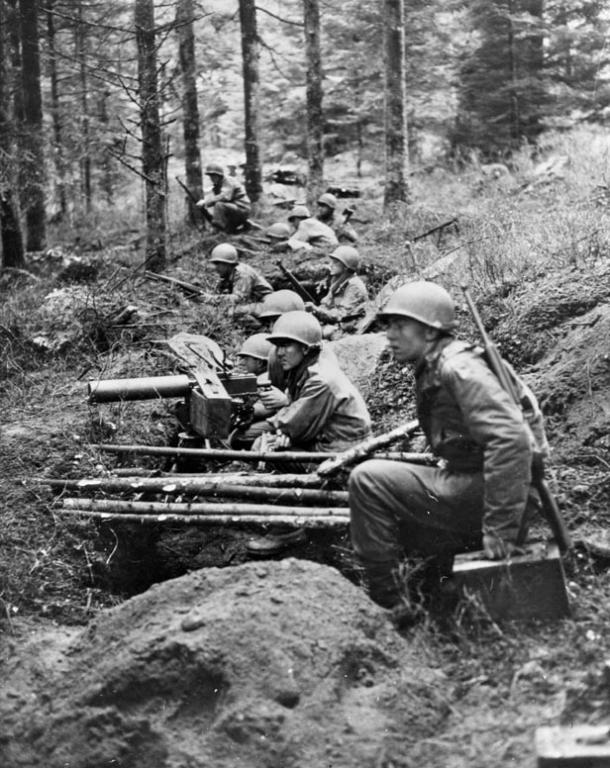
Information
Information

Warning: This is a relatively older thread
This discussion is older than 360 days. Some information contained in it may no longer be current.
- Knowledge Library

- MKL Entry of the Month
- Australia
- Austro-Hungarian Empire
- Canada
- Czechoslovakia
- Denmark
- Finland
- France/Belgium
- Germany
- Italy
- Japan
- Norway
- Russia
- South America
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- United Kingdom
- United States
- Yugoslavia
- Is my rifle authentic or a fake?
- Jay Currah's Lee Enfield Web Site
- On-line Service Records (Canada)
- Technical Articles/Research
- Forum
- Classifieds

- What's New?
-
Photo Gallery

- Photo Gallery Options
- Photo Gallery Home
- Search Photo Gallery List
-
Photo Gallery Search
- Video Club

- iTrader










 PM
PM